# Vue.js 的 template 编译
# $mount
首先看一下 mount 的代码
/*把原本不带编译的$mount方法保存下来,在最后会调用。*/
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount;
/*挂载组件,带模板编译*/
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean): Component {
el = el && query(el);
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
warn(`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`);
return this;
}
const options = this.$options;
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
/*处理模板templete,编译成render函数,render不存在的时候才会编译template,否则优先使用render*/
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template;
/*template存在的时候取template,不存在的时候取el的outerHTML*/
if (template) {
/*当template是字符串的时候*/
if (typeof template === 'string') {
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
template = idToTemplate(template);
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) {
warn(`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`, this);
}
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
/*当template为DOM节点的时候*/
template = template.innerHTML;
} else {
/*报错*/
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn('invalid template option:' + template, this);
}
return this;
}
} else if (el) {
/*获取element的outerHTML*/
template = getOuterHTML(el);
}
if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile');
}
/*将template编译成render函数,这里会有render以及staticRenderFns两个返回,这是vue的编译时优化,static静态不需要在VNode更新时进行patch,优化性能*/
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(
template,
{
shouldDecodeNewlines,
delimiters: options.delimiters
},
this
);
options.render = render;
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns;
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile end');
measure(`${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end');
}
}
}
/*调用const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount保存下来的不带编译的mount*/
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
通过 mount 代码我们可以看到,在 mount 的过程中,如果 render 函数不存在(render 函数存在会优先使用 render)会将 template 进行 compileToFunctions 得到 render 以及 staticRenderFns。譬如说手写组件时加入了 template 的情况都会在运行时进行编译。而 render function 在运行后会返回 VNode 节点,供页面的渲染以及在 update 的时候 patch。接下来我们来看一下 template 是如何编译的。
# 一些基础
首先,template 会被编译成 AST,那么 AST 是什么?
在计算机科学中,抽象语法树(abstract syntax tree 或者缩写为 AST),或者语法树(syntax tree),是源代码的抽象语法结构的树状表现形式,这里特指编程语言的源代码。具体可以查看抽象语法树。
AST 会经过 generate 得到 render 函数,render 的返回值是 VNode,VNode 是 Vue 的虚拟 DOM 节点,具体定义如下:
export default class VNode {
tag: string | void;
data: VNodeData | void;
children: ?Array<VNode>;
text: string | void;
elm: Node | void;
ns: string | void;
context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scope
functionalContext: Component | void; // only for functional component root nodes
key: string | number | void;
componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void;
componentInstance: Component | void; // component instance
parent: VNode | void; // component placeholder node
raw: boolean; // contains raw HTML? (server only)
isStatic: boolean; // hoisted static node
isRootInsert: boolean; // necessary for enter transition check
isComment: boolean; // empty comment placeholder?
isCloned: boolean; // is a cloned node?
isOnce: boolean; // is a v-once node?
constructor(
tag?: string,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: ?Array<VNode>,
text?: string,
elm?: Node,
context?: Component,
componentOptions?: VNodeComponentOptions
) {
/*当前节点的标签名*/
this.tag = tag;
/*当前节点对应的对象,包含了具体的一些数据信息,是一个VNodeData类型,可以参考VNodeData类型中的数据信息*/
this.data = data;
/*当前节点的子节点,是一个数组*/
this.children = children;
/*当前节点的文本*/
this.text = text;
/*当前虚拟节点对应的真实dom节点*/
this.elm = elm;
/*当前节点的名字空间*/
this.ns = undefined;
/*编译作用域*/
this.context = context;
/*函数化组件作用域*/
this.functionalContext = undefined;
/*节点的key属性,被当作节点的标志,用以优化*/
this.key = data && data.key;
/*组件的option选项*/
this.componentOptions = componentOptions;
/*当前节点对应的组件的实例*/
this.componentInstance = undefined;
/*当前节点的父节点*/
this.parent = undefined;
/*简而言之就是是否为原生HTML或只是普通文本,innerHTML的时候为true,textContent的时候为false*/
this.raw = false;
/*静态节点标志*/
this.isStatic = false;
/*是否作为跟节点插入*/
this.isRootInsert = true;
/*是否为注释节点*/
this.isComment = false;
/*是否为克隆节点*/
this.isCloned = false;
/*是否有v-once指令*/
this.isOnce = false;
}
// DEPRECATED: alias for componentInstance for backwards compat.
/* istanbul ignore next */
get child(): Component | void {
return this.componentInstance;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
关于 VNode 的一些细节,请参考VNode 节点。
# createCompiler
createCompiler 用以创建编译器,返回值是 compile 以及 compileToFunctions。compile 是一个编译器,它会将传入的 template 转换成对应的 AST、render 函数以及 staticRenderFns 函数。而 compileToFunctions 则是带缓存的编译器,同时 staticRenderFns 以及 render 函数会被转换成 Funtion 对象。
因为不同平台有一些不同的 options,所以 createCompiler 会根据平台区分传入一个 baseOptions,会与 compile 本身传入的 options 合并得到最终的 finalOptions。
# compileToFunctions
首先还是贴一下 compileToFunctions 的代码。
/*带缓存的编译器,同时staticRenderFns以及render函数会被转换成Funtion对象*/
function compileToFunctions(
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions,
vm?: Component
): CompiledFunctionResult {
options = options || {};
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// detect possible CSP restriction
try {
new Function('return 1');
} catch (e) {
if (e.toString().match(/unsafe-eval|CSP/)) {
warn(
'It seems you are using the standalone build of Vue.js in an ' +
'environment with Content Security Policy that prohibits unsafe-eval. ' +
'The template compiler cannot work in this environment. Consider ' +
'relaxing the policy to allow unsafe-eval or pre-compiling your ' +
'templates into render functions.'
);
}
}
}
// check cache
/*有缓存的时候直接取出缓存中的结果即可*/
const key = options.delimiters ? String(options.delimiters) + template : template;
if (functionCompileCache[key]) {
return functionCompileCache[key];
}
// compile
/*编译*/
const compiled = compile(template, options);
// check compilation errors/tips
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (compiled.errors && compiled.errors.length) {
warn(
`Error compiling template:\n\n${template}\n\n` +
compiled.errors.map((e) => `- ${e}`).join('\n') +
'\n',
vm
);
}
if (compiled.tips && compiled.tips.length) {
compiled.tips.forEach((msg) => tip(msg, vm));
}
}
// turn code into functions
const res = {};
const fnGenErrors = [];
/*将render转换成Funtion对象*/
res.render = makeFunction(compiled.render, fnGenErrors);
/*将staticRenderFns全部转化成Funtion对象 */
const l = compiled.staticRenderFns.length;
res.staticRenderFns = new Array(l);
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
res.staticRenderFns[i] = makeFunction(compiled.staticRenderFns[i], fnGenErrors);
}
// check function generation errors.
// this should only happen if there is a bug in the compiler itself.
// mostly for codegen development use
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if ((!compiled.errors || !compiled.errors.length) && fnGenErrors.length) {
warn(
`Failed to generate render function:\n\n` +
fnGenErrors.map(({ err, code }) => `${err.toString()} in\n\n${code}\n`).join('\n'),
vm
);
}
}
/*存放在缓存中,以免每次都重新编译*/
return (functionCompileCache[key] = res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
我们可以发现,在闭包中,会有一个 functionCompileCache 对象作为缓存器。
/*作为缓存,防止每次都重新编译*/
const functionCompileCache: {
[key: string]: CompiledFunctionResult
} = Object.create(null);
2
3
4
在进入 compileToFunctions 以后,会先检查缓存中是否有已经编译好的结果,如果有结果则直接从缓存中读取。这样做防止每次同样的模板都要进行重复的编译工作。
// check cache
/*有缓存的时候直接取出缓存中的结果即可*/
const key = options.delimiters ? String(options.delimiters) + template : template;
if (functionCompileCache[key]) {
return functionCompileCache[key];
}
2
3
4
5
6
在 compileToFunctions 的末尾会将编译结果进行缓存
/*存放在缓存中,以免每次都重新编译*/
return (functionCompileCache[key] = res);
2
# compile
/*编译,将模板template编译成AST、render函数以及staticRenderFns函数*/
function compile(template: string, options?: CompilerOptions): CompiledResult {
const finalOptions = Object.create(baseOptions);
const errors = [];
const tips = [];
finalOptions.warn = (msg, tip) => {
(tip ? tips : errors).push(msg);
};
/*做下面这些merge的目的因为不同平台可以提供自己本身平台的一个baseOptions,内部封装了平台自己的实现,然后把共同的部分抽离开来放在这层compiler中,所以在这里需要merge一下*/
if (options) {
// merge custom modules
/*合并modules*/
if (options.modules) {
finalOptions.modules = (baseOptions.modules || []).concat(options.modules);
}
// merge custom directives
if (options.directives) {
/*合并directives*/
finalOptions.directives = extend(Object.create(baseOptions.directives), options.directives);
}
// copy other options
for (const key in options) {
/*合并其余的options,modules与directives已经在上面做了特殊处理了*/
if (key !== 'modules' && key !== 'directives') {
finalOptions[key] = options[key];
}
}
}
/*基础模板编译,得到编译结果*/
const compiled = baseCompile(template, finalOptions);
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
errors.push.apply(errors, detectErrors(compiled.ast));
}
compiled.errors = errors;
compiled.tips = tips;
return compiled;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
compile 主要做了两件事,一件是合并 option(前面说的将平台自有的 option 与传入的 option 进行合并),另一件是 baseCompile,进行模板 template 的编译。
来看一下 baseCompile
# baseCompile
function baseCompile(template: string, options: CompilerOptions): CompiledResult {
/*parse解析得到AST*/
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options);
/*
将AST进行优化
优化的目标:生成模板AST,检测不需要进行DOM改变的静态子树。
一旦检测到这些静态树,我们就能做以下这些事情:
1.把它们变成常数,这样我们就再也不需要每次重新渲染时创建新的节点了。
2.在patch的过程中直接跳过。
*/
optimize(ast, options);
/*根据AST生成所需的code(内部包含render与staticRenderFns)*/
const code = generate(ast, options);
return {
ast,
render: code.render,
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
baseCompile 首先会将模板 template 进行 parse 得到一个 AST,再通过 optimize 做一些优化,最后通过 generate 得到 render 以及 staticRenderFns。
# parse
parse 的源码可以参见https://github.com/answershuto/learnVue/blob/master/vue-src/compiler/parser/index.js#L53。
parse 会用正则等方式解析 template 模板中的指令、class、style 等数据,形成 AST。
# optimize
optimize 的主要作用是标记 static 静态节点,这是 Vue 在编译过程中的一处优化,后面当 update 更新界面时,会有一个 patch 的过程,diff 算法会直接跳过静态节点,从而减少了比较的过程,优化了 patch 的性能。
# generate
generate 是将 AST 转化成 render funtion 字符串的过程,得到结果是 render 的字符串以及 staticRenderFns 字符串。
至此,我们的 template 模板已经被转化成了我们所需的 AST、render function 字符串以及 staticRenderFns 字符串。
# 举个例子
来看一下这段代码的编译结果
<div class="main" :class="bindClass">
<div>{{text}}</div>
<div>hello world</div>
<div v-for="(item, index) in arr">
<p>{{item.name}}</p>
<p>{{item.value}}</p>
<p>{{index}}</p>
<p>---</p>
</div>
<div v-if="text">
{{text}}
</div>
<div v-else></div>
</div>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
转化后得到 AST,如下图:
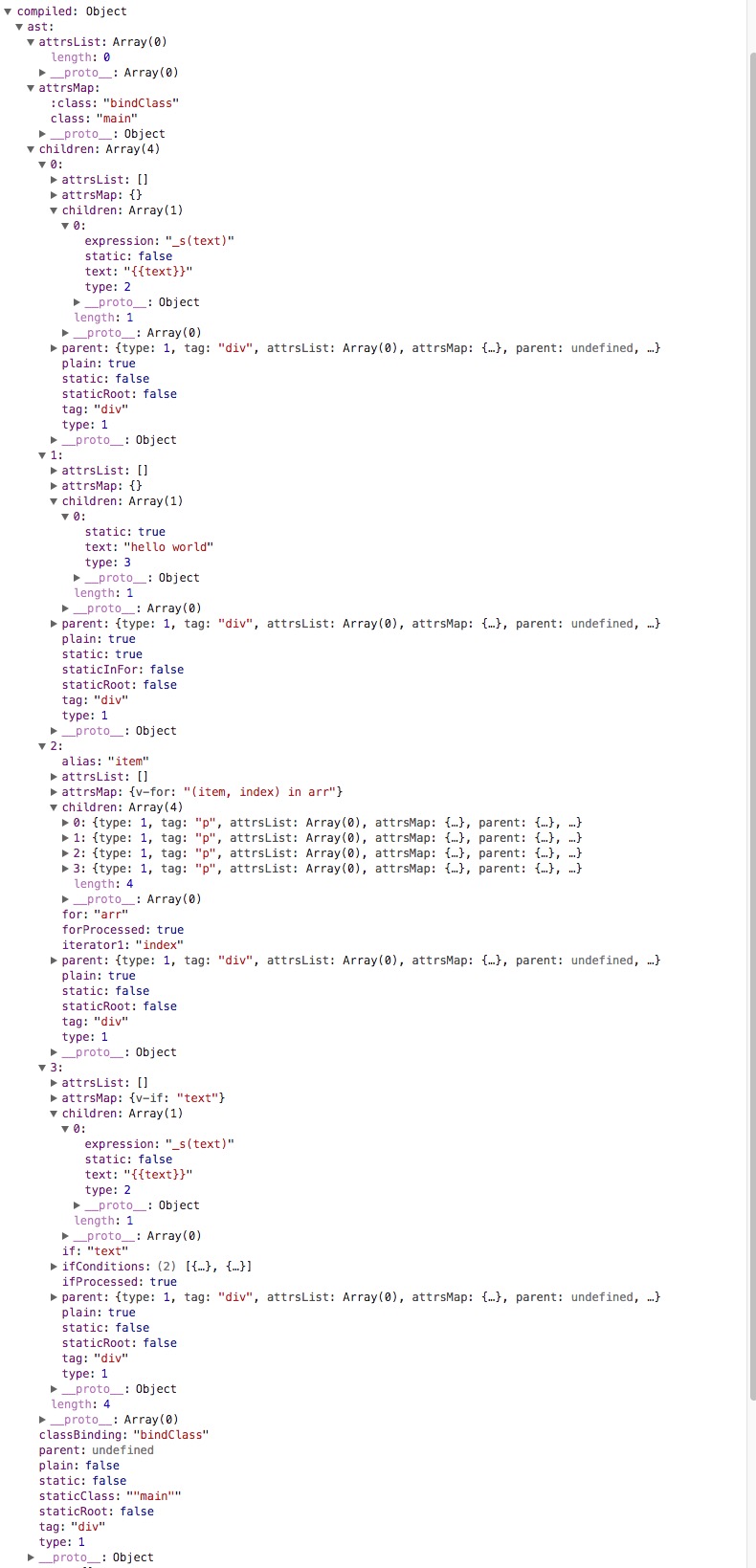
我们可以看到最外层的 div 是这颗 AST 的根节点,节点上有许多数据代表这个节点的形态,比如 static 表示是否是静态节点,staticClass 表示静态 class 属性(非 bind:class)。children 代表该节点的子节点,可以看到 children 是一个长度为 4 的数组,里面包含的是该节点下的四个 div 子节点。children 里面的节点与父节点的结构类似,层层往下形成一棵 AST。
再来看看由 AST 得到的 render 函数
with (this) {
return _c(
'div',
{
/*static class*/
staticClass: 'main',
/*bind class*/
class: bindClass
},
[
_c('div', [_v(_s(text))]),
_c('div', [_v('hello world')]),
/*这是一个v-for循环*/
_l(arr, function (item, index) {
return _c('div', [
_c('p', [_v(_s(item.name))]),
_c('p', [_v(_s(item.value))]),
_c('p', [_v(_s(index))]),
_c('p', [_v('---')])
]);
}),
/*这是v-if*/
text ? _c('div', [_v(_s(text))]) : _c('div', [_v('no text')])
],
2
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# _c,_v,_s,_q
看了 render function 字符串,发现有大量的_c,_v,_s,_q,这些函数究竟是什么?
带着问题,我们来看一下core/instance/render。
/*处理v-once的渲染函数*/
Vue.prototype._o = markOnce;
/*将字符串转化为数字,如果转换失败会返回原字符串*/
Vue.prototype._n = toNumber;
/*将val转化成字符串*/
Vue.prototype._s = toString;
/*处理v-for列表渲染*/
Vue.prototype._l = renderList;
/*处理slot的渲染*/
Vue.prototype._t = renderSlot;
/*检测两个变量是否相等*/
Vue.prototype._q = looseEqual;
/*检测arr数组中是否包含与val变量相等的项*/
Vue.prototype._i = looseIndexOf;
/*处理static树的渲染*/
Vue.prototype._m = renderStatic;
/*处理filters*/
Vue.prototype._f = resolveFilter;
/*从config配置中检查eventKeyCode是否存在*/
Vue.prototype._k = checkKeyCodes;
/*合并v-bind指令到VNode中*/
Vue.prototype._b = bindObjectProps;
/*创建一个文本节点*/
Vue.prototype._v = createTextVNode;
/*创建一个空VNode节点*/
Vue.prototype._e = createEmptyVNode;
/*处理ScopedSlots*/
Vue.prototype._u = resolveScopedSlots;
/*创建VNode节点*/
vm._c = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
通过这些函数,render 函数最后会返回一个 VNode 节点,在_update 的时候,经过 patch 与之前的 VNode 节点进行比较,得出差异后将这些差异渲染到真实的 DOM 上。
